Introduction
In the fast-paced world of medical technology, intensive care medical device prototyping stands as a cornerstone of innovation. The ability to transform an idea into a life-saving product is not just about creativity but also precision, compliance, and functionality. Prototyping for intensive care devices demands a unique approach due to the critical environments in which these devices operate. This article provides a step-by-step guide to navigating the complexities of prototyping intensive care medical devices, ensuring they move from idea to impactful implementation.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Importance of Prototyping in Intensive Care Devices
or intensive care medical devices, where patient lives depend on flawless functionality, intensive care medical device prototyping plays a critical role in ensuring reliability, usability, and compliance.
Key benefits include:
- Early Detection of Design Flaws: Identifying issues during the prototype stage avoids costly revisions during production.
- Enhanced User-Centered Design: Prototypes allow testing with end-users, ensuring devices meet the practical needs of healthcare professionals.
- Streamlined Regulatory Approval: Iterative intensive care medical device prototyping aligns the design with FDA and ISO standards, easing the path to market.
Step 1: Ideation and Conceptual Design
The process begins with a clear understanding of the clinical problem. Intensive care units (ICUs) have specific demands, such as devices that operate seamlessly in high-pressure environments.
Questions to Address During Ideation:
- What clinical problem does the device solve?
- Who are the primary users (e.g., nurses, physicians)?
- What existing devices could your prototype improve upon?
Tools and Methods:
- Brainstorming Sessions: IInclude cross-disciplinary teams to encourage diverse perspectives in intensive care medical device prototyping.
- SWOT Analysis: Identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats for your concept.
- Sketching and Wireframing: Visualize the device’s form and functionality.
Step 2: Defining Requirements
Defining precise requirements ensures your prototype aligns with regulatory, clinical, and user expectations. Effective intensive care medical device prototyping begins with comprehensive requirements documentation.
Key Aspects to Define:
- Functional Requirements: What tasks must the device perform?
- Safety Standards: What fail-safes are necessary for intensive care environments?
- Environmental Conditions: Will the device operate under extreme temperatures or humidity?
Regulatory bodies like the FDA often require a Design Input Document (DID) at this stage. This document outlines all specifications the device must meet.
Step 3: Developing the First Prototype
The first prototype, often called a proof-of-concept, focuses on validating core functionalities. At this stage, aesthetics are secondary to functionality and feasibility.
Steps in Building the First Prototype:
- Choose the Right Materials: Select materials that mimic the final product but allow for flexibility and iteration.
- Use Rapid Prototyping Techniques: 3D printing, CNC machining, and laser cutting can accelerate development.
- Incorporate Modular Design: Modular components allow quick testing and replacement of parts.
Step 4: Iterative Testing and Refinement
Prototyping for intensive care devices involves rigorous testing to meet both performance and regulatory standards.
Testing Criteria:
- Usability Testing: Simulate ICU scenarios to evaluate device interaction.
- Safety Testing: Ensure compliance with standards such as IEC 60601 for electrical safety.
- Durability Testing: Assess performance under stress, including continuous operation over extended periods.
Refinement Through Feedback:
Engage clinicians early in the process. Feedback from end-users often reveals critical design flaws and usability issues.
Step 5: Building a Pre-Production Prototype
Once the initial prototype is refined, the next step is creating a pre-production prototype that closely resembles the final product.
Key Considerations:
- Material Selection: Use biocompatible and sterilizable materials where necessary.
- Manufacturing Processes: Simulate production methods to identify scalability challenges.
- Integration of Software: Ensure that any embedded systems or software are functioning reliably.
Step 6: Navigating Regulatory Requirements
Prototyping for intensive care medical devices must align with stringent regulatory standards to gain market approval.
Key Regulatory Steps:
- Risk Management: Develop a comprehensive risk analysis plan per ISO 14971.
- Clinical Validation: Conduct preclinical and clinical tests to prove safety and efficacy.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed records, including design history files (DHF) and device master records (DMR).
For devices entering the U.S. market, the FDA’s 510(k) or PMA (Premarket Approval) pathways often apply. Ensure your prototype incorporates all necessary design controls and validations.
Step 7: Transitioning to Manufacturing
With a validated prototype in hand, the focus shifts to manufacturing. Intensive care devices require precision manufacturing processes to ensure every unit meets stringent quality standards.
Key Manufacturing Strategies:
- Design for Manufacturability (DFM): Optimize the design for efficient production without compromising quality.
- Supplier Management: Choose suppliers experienced in producing medical-grade components.
- Quality Control: Implement robust quality assurance processes to meet ISO 13485 standards.
Case Studies in Intensive Care Medical Device Prototyping
Case Study 1: Portable Ventilator
A client approached with the need for a compact, portable ventilator for ICUs during emergencies. Prototyping involved:
- Iterative user testing with ICU clinicians.
- Compliance with ISO 80601-2-12 for ventilatory support devices.
- Successful FDA 510(k) clearance within a year.
Case Study 2: Smart IV Pump
This device integrated IoT technology to improve medication delivery accuracy in ICUs. Key steps included:
- Rapid prototyping to refine user interface design.
- Rigorous testing to meet IEC standards for electromagnetic compatibility.
- Pre-production prototype approved after clinical trials.
Challenges in Intensive Care Medical Device Prototyping
1. Stringent Safety Standards
Intensive care devices must meet some of the highest safety and reliability standards, making prototyping both complex and time-consuming.
2. Regulatory Hurdles
Navigating the FDA or EU MDR approval processes can be daunting, especially for startups with limited resources.
3. Cost Constraints
Developing prototypes for intensive care devices can be resource-intensive, requiring careful budget management.
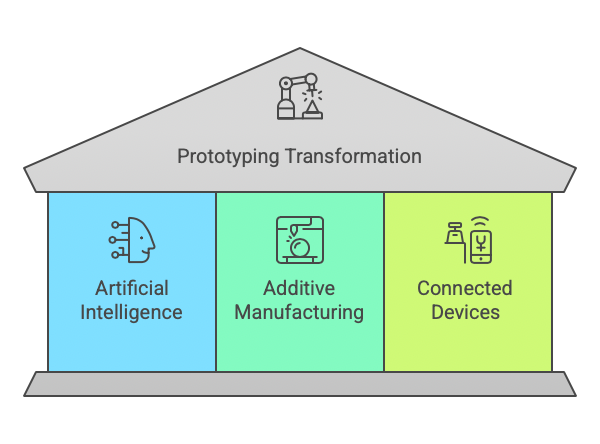
Future Trends in Intensive Care Medical Device Prototyping
1. AI-Driven Prototyping
Artificial intelligence is transforming prototyping by enabling predictive modeling and simulation of device performance.
2. Additive Manufacturing
Advancements in 3D printing allow for faster, more cost-effective prototyping.
3. Connected Devices
The integration of IoT in intensive care devices is increasing, requiring more sophisticated prototyping techniques.
Conclusion
Prototyping intensive care medical devices is a meticulous yet rewarding process. It demands a deep understanding of clinical needs, regulatory requirements, and advanced engineering techniques. By following a structured approach, innovators can bring impactful, life-saving devices to market with confidence.
As a company specializing in medical device development, we’ve worked on projects ranging from portable ventilators to smart crutches, ensuring every prototype not only meets but exceeds industry standards.
If you’re embarking on your intensive care medical device prototyping journey, contact us for expert guidance in transforming your ideas into impactful solutions.
Cross-link: Explore our comprehensive Medical Device Engineering Guide for deeper insights into developing innovative healthcare solutions.



