The journey from concept to market for a medical device is long and complex, with numerous challenges along the way. However, successful medical device commercialization offers immense opportunities to revolutionize patient care, improve health outcomes, and tap into a rapidly growing market. For medical device developers, entrepreneurs, and manufacturers, effectively commercializing a product is key to unlocking its full market potential.
In this comprehensive article, we will explore the medical device commercialization process in detail, offering insights into the essential steps, strategies, and best practices that lead to successful market entry. Whether you’re developing a diagnostic tool, therapeutic device, or wellness product, understanding how to navigate the commercialization phase will help bring your innovations to healthcare professionals and patients around the world.
What is Medical Device Commercialization?
Medical device commercialization refers to the process of bringing a medical device to market after its development and regulatory approval. It encompasses all activities that transform an innovative medical device from an idea or prototype into a commercially viable product available to healthcare providers and patients. This process involves several critical stages, including:
- Regulatory Approval: Ensuring the device meets regulatory standards set by authorities like the FDA (U.S.), EMA (Europe), or other national regulatory bodies.
- Manufacturing and Scaling: Setting up manufacturing processes that can produce the device at scale while maintaining quality.
- Market Entry Strategy: Creating a go-to-market strategy to promote the device and ensure it reaches the right customers.
- Post-Market Surveillance: Ongoing monitoring of the device after it’s on the market to ensure continued safety and performance.
Successfully navigating the commercialization phase is crucial to ensuring that your device has a meaningful impact on healthcare while achieving financial success.
Key Steps in Medical Device Commercialization
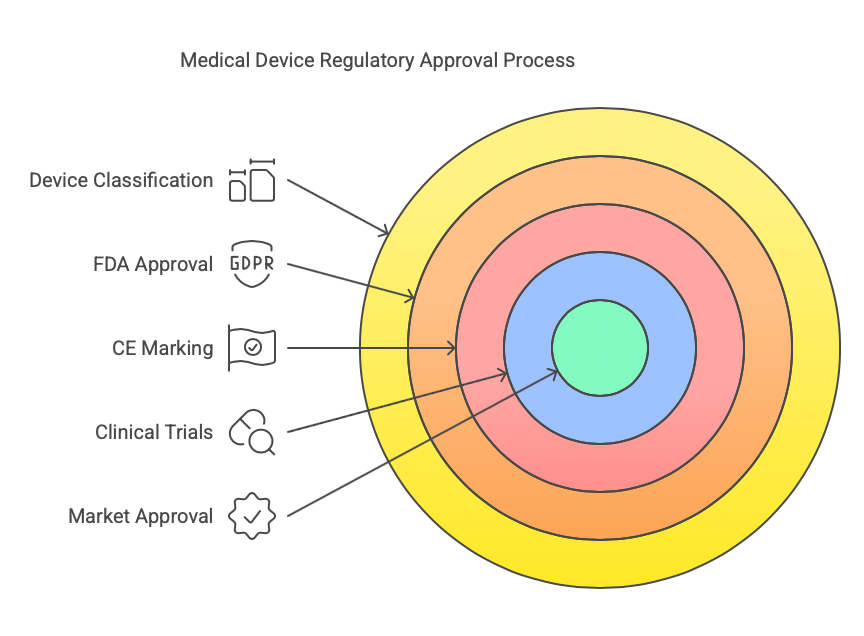
1. Understanding Regulatory Pathways and Requirements
Understanding Regulatory Pathways and Requirements The regulatory pathway is one of the most critical aspects of medical device commercialization. Different countries have different regulatory requirements for medical devices, and navigating these requirements can be complex. Regulatory approval ensures that the device is safe, effective, and reliable.
Steps for Regulatory Approval:
- Classify the Device: Medical devices are classified into different risk categories (Class I, II, or III) based on their intended use and risk to the patient. The classification affects the approval process.
- FDA Approval (U.S.): In the U.S., the FDA regulates medical devices. Class I devices generally require less regulatory scrutiny, while Class II and III devices often require more extensive clinical trials and premarket approval.
- CE Marking (Europe): For devices sold in the European Union, obtaining a CE mark demonstrates compliance with EU medical device regulations. This process includes conformity assessments, clinical evaluations, and testing.
- Clinical Trials: Some devices, particularly those in higher-risk categories, require clinical trials to demonstrate their safety and effectiveness before they can be marketed.
Tips for Regulatory Success:
- Start early by understanding the regulatory requirements of your target markets.
- Work closely with regulatory experts to streamline the approval process.
- Maintain thorough documentation to ensure compliance and facilitate approvals.
- Consider how each regulatory decision impacts overall medical device commercialization timelines and budget allocation.
- Integrate regulatory milestones into your broader medical device commercialization plan to ensure alignment across all business function
2. Scaling Manufacturing and Quality Control
Once your device has received regulatory approval, it’s time to focus on scaling manufacturing. This involves setting up processes that can efficiently produce the device in large quantities while maintaining high standards of quality. Medical device commercialization requires ensuring that each unit of the device is produced to the highest safety and performance standards.
Key Manufacturing Considerations:
- Supplier Selection: Choose suppliers who can provide high-quality materials that meet regulatory standards. Your device’s components must be reliable and safe.
- Process Validation: Validate the manufacturing process to ensure that each device consistently meets quality standards. This may involve testing different production methods and materials.
- Quality Control: Implement robust quality control measures to ensure that all devices produced meet the required safety, functionality, and performance criteria.
Tips for Manufacturing Success:
- Invest in automated systems to increase efficiency and reduce human error.
- Regularly audit your manufacturing processes and suppliers to ensure compliance.
- Consider partnering with contract manufacturers if you lack the capacity to scale production in-house.
3. Developing a Market Entry Strategy
Developing a strong market entry strategy is critical for the success of any medical device commercialization. A solid strategy helps ensure that your product reaches the right customers—whether they are hospitals, clinics, or patients—and that the device is positioned effectively in a competitive market.
Key Elements of a Market Entry Strategy:
- Target Market Segmentation: Identify the specific market segments (e.g., hospitals, clinics, outpatient centers, homecare) where your device will have the greatest impact.
- Pricing Strategy: Determine a pricing model that is competitive while still allowing for profitability. Consider factors such as manufacturing costs, competitor pricing, and reimbursement structures.
- Sales and Distribution Channels: Select the best channels for distributing your device. Options include direct sales, partnerships with distributors, or selling through online platforms.
- Marketing and Promotion: Develop a marketing plan that includes both online and offline strategies. Consider attending trade shows, creating educational content, and reaching out to key opinion leaders in the medical community.
Tips for Market Entry Success:
- Collaborate with healthcare professionals and organizations to gain insights into market needs and build trust in your product.
- Use data-driven approaches to identify market opportunities and potential partnerships.
- Invest in educating potential customers on the benefits and features of your device.
4. Navigating Reimbursement Pathways
In many healthcare systems, especially in the U.S. and Europe, reimbursement plays a key role in the success of a medical device. If your device is not reimbursed or covered by insurance, patients and healthcare providers may be reluctant to adopt it. Understanding the reimbursement pathways and ensuring that your device is eligible for coverage is a critical part of the commercialization process.
Key Reimbursement Considerations:
- Healthcare Policy: Understand the reimbursement policies in your target markets. In the U.S., Medicare and private insurance companies often determine reimbursement rates for medical devices.
- Coding and Pricing: Devices may require specific coding for reimbursement purposes. Work with health insurers to determine appropriate billing codes and ensure they’re in place before launching.
- Clinical Evidence: Having robust clinical evidence to support the efficacy and cost-effectiveness of your device can help secure reimbursement.
Tips for Navigating Reimbursement:
- Work with reimbursement experts to ensure that your device meets the requirements for insurance coverage.
- Gather strong clinical evidence to demonstrate the value of your device to both healthcare providers and insurers.
- Keep up with policy changes and adapt your strategy as needed.
5. Post-Market Surveillance and Continuous Improvement
Once your medical device is on the market, the work is far from over. Post-market surveillance is a critical aspect of medical device commercialization. This phase involves monitoring the device’s performance in the real world, gathering feedback, and identifying any potential issues that may arise.
Key Post-Market Surveillance Activities:
- Collecting Data: Monitor your device’s performance through clinical feedback, patient reports, and real-world data collection. This can help identify any safety issues or improvements that can be made.
- Adverse Event Reporting: Report any adverse events or device malfunctions to regulatory authorities as required.
- Continuous Improvement: Use the feedback gathered during the post-market phase to make necessary improvements, whether it’s modifying the device design, improving manufacturing processes, or enhancing customer support.
Tips for Post-Market Success:
- Set up a system to capture feedback from healthcare providers and patients in real time.
- Be transparent about product performance and address any concerns quickly.
- Regularly review post-market data and make updates or changes as necessary to maintain device quality and safety.
- Establish a dedicated team focused on medical device commercialization strategy refinement based on market performance.
- Consider how your medical device commercialization timeline affects long-term product viability and plan accordingly.
Conclusion
Medical device commercialization is a multifaceted process that involves overcoming significant challenges and making strategic decisions across regulatory approval, manufacturing, market entry, and post-market surveillance. By following the right steps, building strong partnerships, and focusing on delivering a high-quality, innovative product, you can unlock the full potential of your medical device in the healthcare market.
From understanding regulatory requirements and ensuring product quality to developing a market strategy and managing reimbursement, the commercialization of medical devices requires a comprehensive approach that integrates all aspects of the product lifecycle. By staying proactive, responsive to feedback, and continuously improving your processes, you can position your device for long-term success in a competitive and rapidly evolving market. The medical device commercialization journey doesn’t end at launch—rather, it transforms into an ongoing cycle of refinement and optimization.
How are you currently approaching the commercialization process for your medical device? What challenges have you faced, and how have you overcome them to ensure market success?



 430 Park Ave, New York, NY 10022, USA
430 Park Ave, New York, NY 10022, USA Paevalille tn 6, Office 84, Estonia, Tallinn, 13517
Paevalille tn 6, Office 84, Estonia, Tallinn, 13517 Barykadna St 7, Dnipro, Ukraine, 49000
Barykadna St 7, Dnipro, Ukraine, 49000