In the medical device industry, precision and reliability are non-negotiable. When issues arise, identifying the root cause quickly and effectively is critical. This is where RCA Tools (Root Cause Analysis tools) play a transformative role. By equipping teams with structured methods to pinpoint and address problems, RCA tools ensure enhanced product quality, regulatory compliance, and patient safety.
This comprehensive guide explores the importance of RCA tools, their applications in medical device development, and actionable strategies for leveraging them to revolutionize problem-solving within your team.
Table of Contents
What Are RCA Tools?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) tools are methodologies and techniques used to uncover the underlying causes of problems rather than just addressing symptoms. These tools provide structured approaches to:
- Identify the root cause of an issue.
- Implement permanent solutions to prevent recurrence.
- Streamline troubleshooting processes.
In medical device teams, RCA tools are invaluable for ensuring regulatory compliance, maintaining product quality, and addressing complex issues in design, manufacturing, and post-market surveillance.
Why Are RCA Tools Essential for Medical Device Teams?
The medical device industry operates under stringent regulations, such as FDA’s 21 CFR Part 820 and ISO 13485 standards. RCA tools enable teams to:
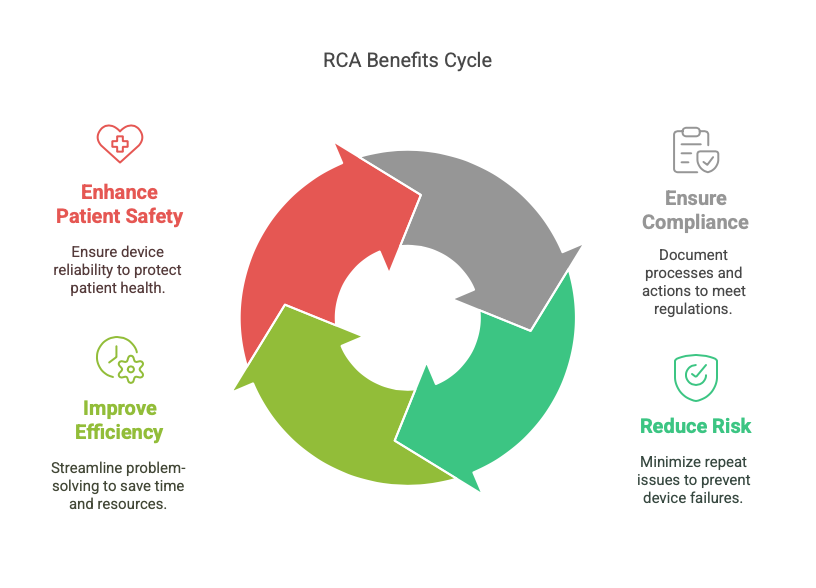
- Ensure Compliance: RCA tools help document processes and corrective actions, aligning with regulatory requirements.
- Reduce Risk: Addressing root causes minimizes the likelihood of repeat issues, reducing risks associated with device failure.
- Improve Efficiency: RCA tools streamline problem-solving, saving time and resources.
- Enhance Patient Safety: By resolving root causes, teams can ensure devices perform reliably, safeguarding patient health.
Top RCA Tools for Medical Device Teams
1. Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa Diagram)
Overview:
The fishbone diagram visualizes the potential causes of a problem, organizing them into categories such as People, Processes, Materials, and Equipment.
Application:
- Use during brainstorming sessions to identify potential failure points in design or manufacturing.
Pros:
- Easy to use and understand.
- Encourages team collaboration.
Cons:
- Limited depth for complex problems.
- Requires additional tools for deeper analysis.
2. 5 Whys Analysis
Overview:
This iterative questioning technique delves into the root cause by repeatedly asking “Why?” until the fundamental issue is uncovered.
Application:
- Ideal for investigating human error or process failures.
Pros:
- Simple and quick to implement.
- Encourages a deeper understanding of problems.
Cons:
- May oversimplify complex issues.
- Effectiveness depends on facilitator expertise.
3. Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Overview:
FMEA identifies potential failure modes, evaluates their impact, and prioritizes corrective actions based on risk levels.
Application:
- Critical for assessing risks in device design, manufacturing, and testing.
Pros:
- Comprehensive risk assessment.
- Helps prioritize issues by severity.
Cons:
- Time-intensive.
- Requires cross-functional team collaboration.
4. Pareto Analysis
Overview:
Based on the 80/20 rule, Pareto analysis identifies the most significant factors causing a problem.
Application:
- Effective for post-market surveillance to address recurring customer complaints.
Pros:
- Focuses on high-impact issues.
- Data-driven approach.
Cons:
- Requires accurate data.
- Does not identify root causes on its own.
5. Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)
Overview:
FTA is a top-down approach that uses Boolean logic to map out potential failure points leading to a problem.
Application:
- Suitable for complex, system-level issues in medical devices.
Pros:
- Provides a detailed visual representation.
- Useful for risk management and regulatory audits.
Cons:
- Complex and time-consuming.
- Requires expertise in system-level analysis.
Practical Tips for Implementing RCA Tools
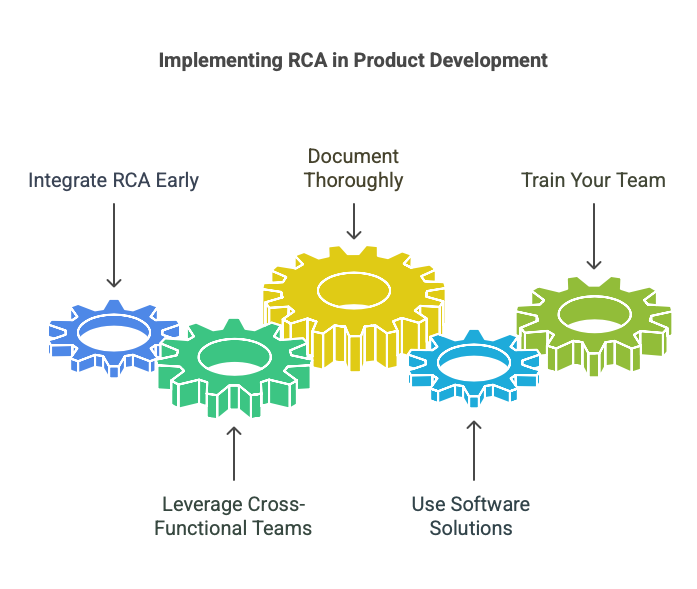
- Integrate RCA Early: Start using RCA tools during the design and development phases to address potential issues proactively.
- Leverage Cross-Functional Teams: Involve engineers, quality assurance, and regulatory experts to gain diverse perspectives.
- Document Thoroughly: Maintain detailed records of RCA processes, findings, and corrective actions for regulatory audits.
- Use Software Solutions: Invest in RCA software to streamline analysis, improve accuracy, and ensure traceability.
- Train Your Team: Provide ongoing training to ensure team members can effectively use RCA tools.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Challenge 1: Lack of Expertise
Solution:
- Conduct training sessions and workshops.
- Use external consultants for complex analyses.
Challenge 2: Incomplete Data
Solution:
- Implement robust data collection processes.
- Use tools like IoT sensors to monitor device performance in real-time.
Challenge 3: Resistance to Change
Solution:
- Demonstrate the ROI of RCA tools.
- Share success stories to gain buy-in from stakeholders.
RCA Tools in Action: A Medtech Case Study
Scenario: A wearable cardiac monitor experiences frequent data transmission failures.
Approach:
- Use a Fishbone Diagram to categorize potential causes (e.g., hardware, software, connectivity).
- Apply the 5 Whys to investigate specific issues in the firmware.
- Conduct FMEA to assess risk and prioritize fixes.
Outcome: By addressing firmware bugs and optimizing the wireless module, the team reduced failure rates by 85%, ensuring reliable data transmission.
Conclusion
RCA tools are indispensable for medical device teams aiming to revolutionize problem-solving. By implementing structured analysis methods like the Fishbone Diagram, 5 Whys, and FMEA, teams can uncover root causes, address issues proactively, and enhance device performance. While challenges exist, proper training, documentation, and a culture of continuous improvement can unlock the full potential of RCA tools.
Ready to optimize your problem-solving processes with RCA tools? Start today to ensure your medical devices meet the highest standards of quality and reliability.




 430 Park Ave, New York, NY 10022, USA
430 Park Ave, New York, NY 10022, USA Paevalille tn 6, Office 84, Estonia, Tallinn, 13517
Paevalille tn 6, Office 84, Estonia, Tallinn, 13517 Barykadna St 7, Dnipro, Ukraine, 49000
Barykadna St 7, Dnipro, Ukraine, 49000